National Funded Research Projects of Md. Nazrul Islam
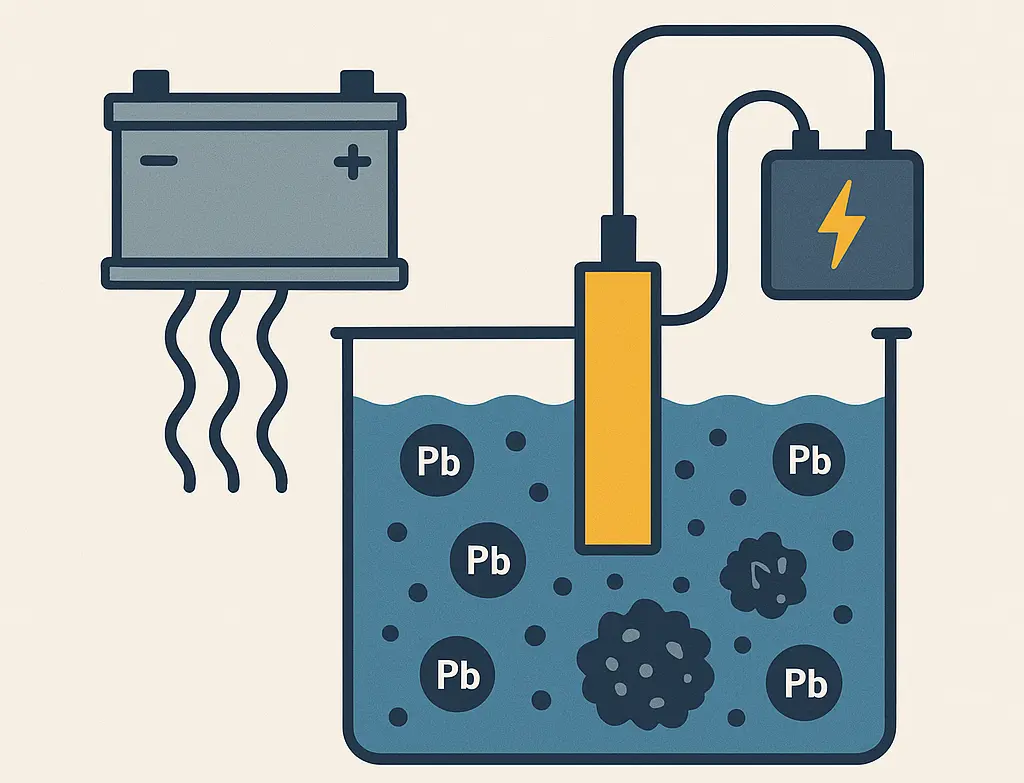
1. Electrocoagulation for Lead Removal from Battery Effluent
Description: This project developed an electrocoagulation (EC) technique to remove lead from battery industry effluents, a significant pollutant in Bangladesh. Laboratory experiments optimized EC parameters to achieve high lead removal efficiency, reducing environmental and health risks.
Funding Source: University Grants Commission (UGC) of Bangladesh (inferred).
Publication: Rahman, S.H., Islam, M.N., et al., Journal of Bangladesh Academy of Sciences, Vol. 39, No. 2, pp. 125-134, 2015.
Impact: Supports Bangladesh’s efforts to control industrial pollution, offering a scalable solution for lead-contaminated wastewater.
Keywords: Electrocoagulation, Lead Removal, Battery Effluent, Water Pollution.
Image: No project-specific images are available in the sources. A potential image could depict an electrocoagulation setup with electrodes in a lab reactor. Would you like me to generate such an image?
2. Reuse of Electrocoagulated Metal Hydroxide Sludge (EMHS) from Textile Industry
Description: This study explored reusing electrocoagulated metal hydroxide sludge (EMHS) from textile wastewater as a construction material, promoting sustainable waste management. Geotechnical tests assessed EMHS’s suitability for building blocks.
Funding Source: Ministry of Science and Technology, Bangladesh (inferred).
Publication: Adyel, T.M., Islam, M.N., et al., Journal of Waste Management, Article ID 686981, 2013.
Impact: Reduces landfill waste and supports sustainable construction, aligning with Bangladesh’s circular economy goals.
Keywords: Electrocoagulation, Textile Industry, Waste Reuse, Sustainable Construction.
Image: No images provided in sources. A relevant image could show textile sludge samples or a prototype building block made from EMHS. Would you like me to generate this image?
3. Analysis of Heavy Metal Content in Textile Industry Sludge
Description: This project used Energy Dispersive X-Ray Fluorescence (EDXRF) to quantify heavy metals (e.g., chromium, lead) in textile industry sludge, evaluating electrocoagulation’s effectiveness in pollution control.
Funding Source: Bangladesh Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (BCSIR) (inferred).
Publication: Adyel, T.M., Islam, M.N., et al., Metals, Vol. 2, pp. 478-487, 2012.
Impact: Enhances pollution monitoring in Bangladesh’s textile sector, supporting environmental regulations.
Keywords: Heavy Metals, Electrocoagulation, EDXRF, Textile Industry.
Image: No images available. An illustrative image could show an EDXRF spectrometer analyzing sludge samples. Would you like me to generate this image?
4. Electrocoagulation for COD Reduction in Surface Water
Description: This project applied electrocoagulation to reduce Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) in polluted surface water, improving water quality for Bangladesh’s rivers and lakes.
Funding Source: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Bangladesh (inferred).
Publication: Rahman, S.H., Islam, M.N., et al., Bangladesh Journal of Scientific and Industrial Research, Vol. 47(1), pp. 77-82, 2012.
Impact: Provides a cost-effective water treatment method, aiding restoration of polluted water bodies.
Keywords: Electrocoagulation, COD Reduction, Surface Water, Water Treatment.
Image: No images in sources. A potential image could depict a water sample being treated in an EC reactor. Would you like me to generate this image?
5. Seasonal Variations of Arsenic in the Ganges and Brahmaputra Rivers
Description: This study analyzed seasonal arsenic fluctuations in the Ganges and Brahmaputra Rivers using geochemical methods, addressing public health and agricultural risks.
Funding Source: Ministry of Science and Technology, Bangladesh (inferred).
Publication: Islam, S.M.N., Islam, M.N., et al., Journal of Scientific Research, Vol. 4(1), pp. 65-75, 2012.
Impact: Informs water management and public health policies to mitigate arsenic contamination risks.
Keywords: Arsenic Contamination, Ganges River, Brahmaputra River, Geochemical Analysis.
Image: No images available. An image could show river water sampling or arsenic testing equipment. Would you like me to generate this image?
- Chalan Beel Wetlands
- Chemical Fertilizer Use
- Padma River Morphology
- Fakirhat Biodiversity
- Turag River Basin
- Ganges-Kobadak Project
- Tangail Tow
- Bhairab River
- Female Garment Workers
- Toxic Algae Modeling
- Water Crisis in Asia
Nazrul Islam Prantique
Copyright © 2025, Nazrul Islam Prantique. All rights reserved.
